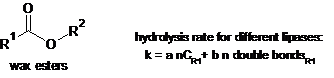Guido Galliani
Gleaner srls, Italy
Title: Why, when, and how to shake off bad reputation from wax esters
Biography
Biography: Guido Galliani
Abstract
Until not so long ago, wax esters had an overall bad reputation. Spermaceti, jojoba oil, orange roughy oil are typical examples of wax esters, well renown insofar that they are used topically, mostly for cosmetic purposes. However, it is equally well known that these products should never be ingested, under penalty of very unpleasant consequences, such as nausea, diarrhoea, and steatorrhea. Some years ago, we started a program to understand some rather contradictory data. It is known that roe (fish eggs) is consumed as a food since time immemorial. This occurs either on roe as is (caviar, lumpfish roe) or after some treatment (Italian bottarga, Greek taramosalata, Japanese karasumi, Scandinavian Lysekils kaviar). Moreover, it was known that wax esters are an important constituent of roe, in some instances the majority component. In spite of this, no concern had ever been raised as to edibility or side effects of such products. The first results in analyzing wax esters from several roe-based foods showed that polyunsaturated fatty acids were a very important component of the acidic moiety. Successive results from other research groups confirmed our original results. These findings partially supported substantiating and launching a commercial product, Calanus® oil, extracted from copepod Calanus finmarchicus, rich in wax esters and in omega-3 polyunsaturated acids. From all this, it is clear that the term wax ester is just a rough chemical definition. Within this class of lipids different molecules are included. Some of them are essentially saturated molecules, primarily intended to assist buoyancy and to store energy. Other molecules represent a more complex metabolism, not yet fully understood. Differences are reflected in the metabolic fate when ingested. Competitive kinetics results will be presented from several wax esters and lipases, revealing suggestions about wax esters as a delivering form for omega- 3.