
Kawthar Alghamdi
UCD Conway Institute - University College Dublin, Ireland
Title: Conjugated linoleic acid induces TGFβ signalling regulate macrophage fate
Biography
Biography: Kawthar Alghamdi
Abstract
The chronic recruitment of monocytes and their subsequent migration through the endothelium contribute to atherosclerotic plaque development, the underlying cause of heart attacks and stroke. A specific blend of conjugated linoleic acid (80:20 cis-9, trans-11: trans-10, cis-12-CLA) has the unique property of inducing regression of pre-established atherosclerosis in vivo via modulation of monocyte function. Currently, there are no therapeutic targets which induce regression of pre-established atherosclerosis. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms through which CLA 80:20 mediates its atheroprotective effect is important for more effective management of this disease. This study aimed to identify novel pathways regulated by CLA, which inhibits monocyte function using a proteomic approach. THP-1 monocytes were treated for 18 h with CLA blend, a lipid control Oleic acid (OA) or DMSO (n=3 per treatment group). Proteins were trypsin-digested prior to analysis by liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution, high mass accuracy Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Global proteomic protein identities and relative quantitation were determined in a label-free approach, using the MaxQuant, Perseus and IPA suite of programs. A total of more than 1500 proteins were identified by mass spectrometry across the experimental groups using Perseus. Following statistical analysis using the t-test, 121 proteins were found to be significantly altered following treatment with CLA 80:20 compared to the control (DMSO). 103 proteins were unique to CLA blend and not altered by OA. Subsequent bioinformatics analysis of the regulated proteins showed enrichment of the TGFβ signalling pathway. Validation of proteomic analysis was performed by Western blot analysis of THP-1 monocytes. Our data revealed that CLA 80:20 blend regulates the TGFβ signaling pathway in monocytes. This work contributes to our understanding of the atheroprotective pathways regulated by CLA 80:20 which impacts on monocyte/macrophage fate.
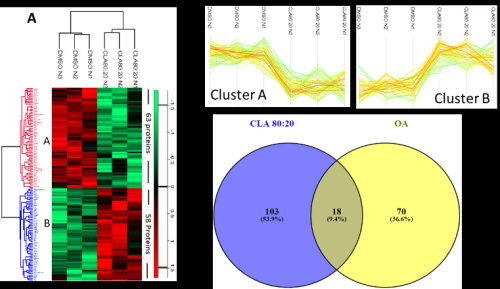
Figure 1: Global Proteomic Analysis: Significant proteins which were altered by CLA blend compared to control were determined by Student’s t-test, where considered significant a p-value < 0.05 (A) Hierarchical clustering global proteomic analysis exhibited only the 121 proteins which were statistically different with CLA relative to the control DMSO, 63 proteins down- regulated (green) and 85 proteins were upregulated(red), it was determined by Student’s t-test, where p< 0.05 flowing with z-score normalization of the median value of logarithmized intensities (Log 2) of each protein profile. Statistical analysis was performed in Perseus software (version 1.5.0.15). (B) Expression profile of the two hierarchical clusters, which were statistically different compare to the control group DMSO. (C) Common and unique number of proteins regulated by CLA blend and OA which were significantly changed compared to the control DMSO for both groups.

