
Calvano Cosima Damiana
Università di Bari, Italy
Title: Development and use of advanced mass spectrometry techniques for the characterization of cellular lipidome profile of fibroblasts in early on-set Parkinson’s disease patients
Biography
Biography: Calvano Cosima Damiana
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease involving the nigrostriatal pathway; patients’ manifest motor symptoms dysfunction when more than 50% of neurons are lost. Though it is well recognized that alterations of lipid signaling, and metabolism plays a significant role in many human diseases, little is known about the role of lipids during this specific disease. Recently, it has been reported that altered lipid pathways in the primary visual cortex and the anterior cingulate are possible in neurological disorders such as PD by analyzing post-mortem tissues from patients in advanced neuronal degeneration stage. Such an approach, however, hinders the identification of the first neuronal changes. Thus, understanding the mechanisms of PD and recognizing neuronal changes in the early phase of PD represents a crucial task. According to their polygenic predisposition and environmental etiopathology skin fibroblasts are today widely recognized as a useful model of primary human cells, capable of reflecting the chronological and biological aging of the patients. A lipidomics study of easily accessible primary human fibroblasts is presented here based on hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization-Fourier transform mass spectrometry, using both positive and negative polarities. Phospholipids (PL) from dermal fibroblasts of two unrelated PD patients with different parkin mutations and two controls were characterized by recurring to single and tandem MS measurements on a hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. This untargeted approach enabled the identification of various PL classes as phosphatidylethanolamines (PE), phosphatidylcholines (PC), sphingomyelins, lysoPC, lysoPE, phosphatidylinositols, phosphatidylserines, mono-, di- and tri-hexosylceramides and ganglioside GM1, GM2 and GM3. To identify the main lipids involved in the pathological condition of PD, lipidomics data on a higher number of samples need to be collected and processed by multivariate statistical analyses. In this communication, an interesting set of preliminary findings will be reported and discussed.
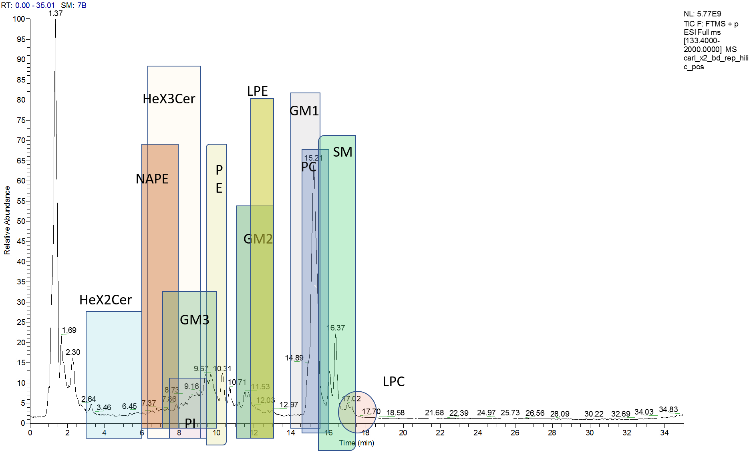
Figure 1. HILIC-ESI (+) MS total ion current chromatogram of a lipid extract from human fibroblasts.

